Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease
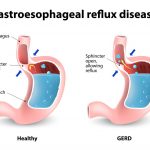
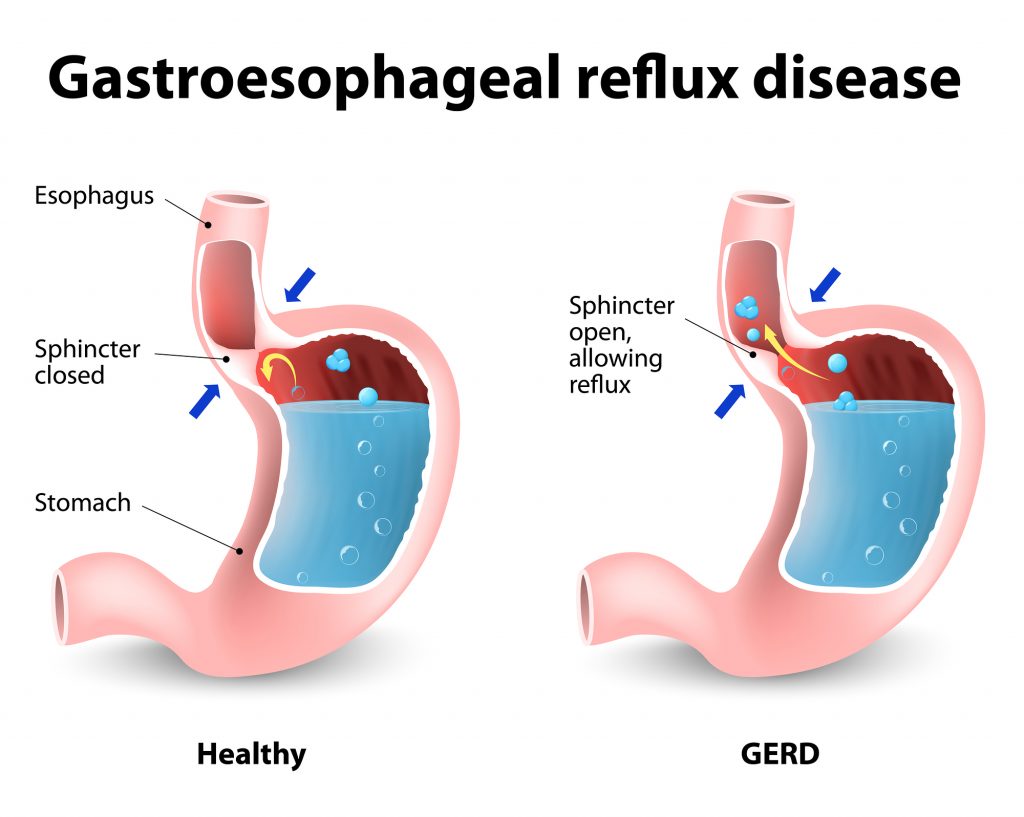
Acid reflux – otherwise known as gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a condition where the natural defences within the body’s upper digestive system are impaired. These defences are in place to prevent the acidic contents of the stomach from entering the oesophagus causing a burning sensation that in laymen’s terms, we call heartburn.
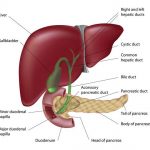
One of the primary causes of this condition is a hiatal hernia – a condition where the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. The other is the damage to the anti-reflux defence mechanisms including the lower oesophageal sphincter (LOS).
Approximately one in five people in the developed western world suffer from GORD and require acid reflux treatment. Prolonged reflux can lead to damage to the lining of the oesophagus causing various complications such as oesophagitis, ulcers and Barrett’s oesophagus.
We are gastro-oesophageal reflux disease specialists and can assist you with your treatment options.
Acid Reflux Treatment
Diagnosis is usually confirmed by tests like gastroscopy, barium swallow x-ray and oesophageal pH and manometry test.
Surgical therapy should be considered, when a diagnosis of reflux, acid or non-acid (or bile reflux), is objectively confirmed and when the patients:
- Have failed medical management (inadequate symptom control, severe regurgitation not controlled with acid suppression).
- Some patients opt for surgery, despite successful medical management to avoid taking medication or if they develop side effects from the medication.
- Due to complications of GORD, including erosive esophagitis, stricture, and/or Barrett’s oesophagus (a condition where the inner lining of the oesophagus changes to that of the stomach lining, due to acid irritation).
- Have extra-oesophageal manifestations, such as asthma, hoarseness, cough, chest pain, and/or aspiration.
Below 18.5 - Underweight
18.5-24.9 - Normal
25.0-29.9 - Overweight
30.0 and Above - Obese
AT THIS STAGE YOU DO NOT QUALIFY FOR WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY, PLEASE
CONTACT US IF YOU HAVE FURTHER QUESTIONS.